Social Media & Mental Health Survey Findings
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
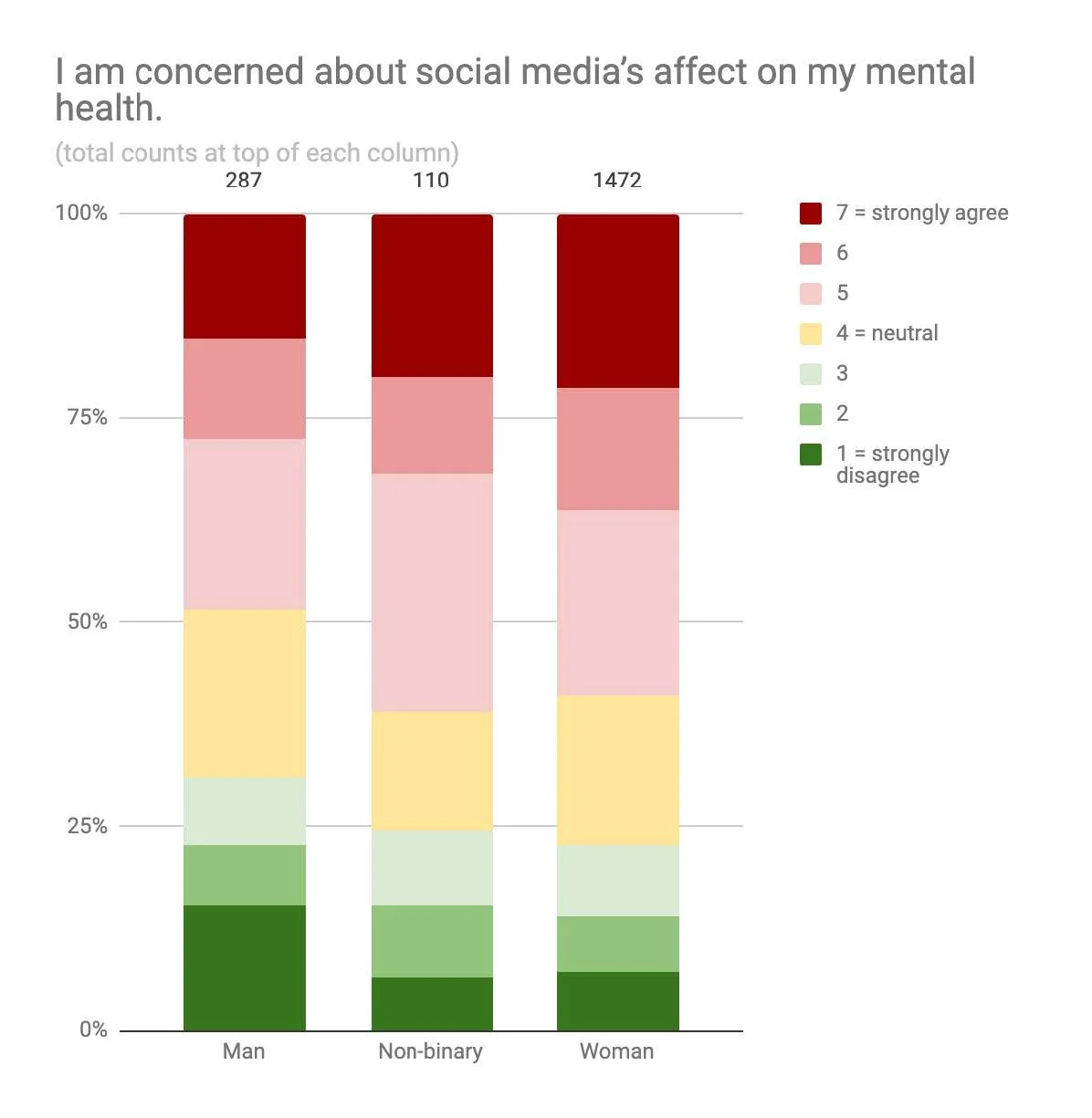
DoSomething’s research shows similar findings as Instagram’s recently leaked internal research: a sizable portion of young people experience negative mental health affects as a result of social media use. The majority (57.5%) of participants in our survey said they are concerned about social media’s affect on their mental health.
DoSomething broke down the mental health effects based on gender and race. Non-binary youth and young women were more concerned about social media’s affect on their mental health compared to young men. Asian, white, and mixed-race respondents were more concerned than Black respondents.
We examined factors that lead to positive mental health effects. Using social media for social connection was reported as the biggest driver of a positive effect (73% agreed that social media helps with connection). Respondents explained that social media is a convenient and fun way to message people, often those who live far away. Occasionally, participants built new connections based on meeting people who shared their interests.
Besides connection, other positive effects of social media included: giving and getting support; generating a sense of belonging; ideas for self-care and self-improvement; helping with self-acceptance; and a place for self-expression. Respondents also liked to use social media to boost their mood by looking at fun and uplifting content. 8% of respondents indicated that social media has no positive effects whatsoever on their mental health.
We also examined factors that lead to negative mental health effects. Risk factors included: comparing themselves to others; feeling pressure to have a “perfect” life; doubting their accomplishments; body- and self-image issues; neglecting self care due to wasting time on social apps; and being exposed to negative content, including oppressive messages and overwhelming news stories. 12% of respondents wrote that social media has no negative effects on their mental health.
Notably, there isn’t a universal effect from social media usage on mental health. More respondents (12%) explained that social media had no negative effects on their mental health compared to those (8%) who said it had no positive effects. And while the majority (57.5%) of young people are concerned about social media‘s affect on their mental health, a sizable amount (42.5%) are neutral or not concerned.
Young people are utilizing an array of tactics to protect their mental health, including limiting social media usage and using social apps primarily for social connection. In rare cases, young people are deleting social apps entirely to protect their mental health.
As a social justice organization, DoSomething also wanted to evaluate how social media affects young people’s outlook and behavior. Participants were asked about how often they learned about current events, important causes, and new volunteer opportunities on social media:
For learning about current events, 64.9% selected often and 26.9% said sometimes.
For learning about important causes, 54.6% selected often and 35.6% said sometimes.
For exposure to advocacy ideas 40.1% selected often and 41.7% said sometimes.
For exposure to volunteer ideas, 25.8% selected often and 44.1% said sometimes.
Our survey had 1,905 participants, aged 13-25, and was conducted in September 2021.